2026 How MPC Wallets & Stablecoins Unlock Just-in-Time Liquidity for Enterprises
Phoebe Duong
Author
By 2026, the conversation is no longer about a “Crypto vs. SWIFT” comparison.
Instead, forward-looking enterprises are building a Hybrid Financial Stack, where each payment rail serves a clearly defined function.
- Banking rails are reserved for large-value, low-frequency transactions that require strict reconciliation and regulatory compliance.
- Stablecoin rails are designed for high-frequency, cross-border cash flows that must be disbursed precisely when economic activity occurs.
In this context, the strategic value of stablecoins does not lie in faster payments.
It lies in their ability to enable Just-in-Time Liquidity, where capital is deployed exactly at the moment real economic value is created.
This article examines that strategic shift. It also explains why, as enterprises move closer to real-time liquidity models, the need for a new governance layer becomes unavoidable, and why MPC wallet infrastructure (Multi-Party Computation) is emerging as a core form of digital custody infrastructure for enterprise-grade security and control.
Just-in-Time Liquidity: The Future of Enterprise Payments Strategy
APAC has emerged as a primary growth engine for digital assets, accounting for nearly 30 percent of global on-chain value, approximately USD 2.36 trillion, with 69 percent year-over-year growth.
At the same time, India, the United States, Pakistan, Vietnam, and Brazil rank as the top five countries in global crypto adoption.
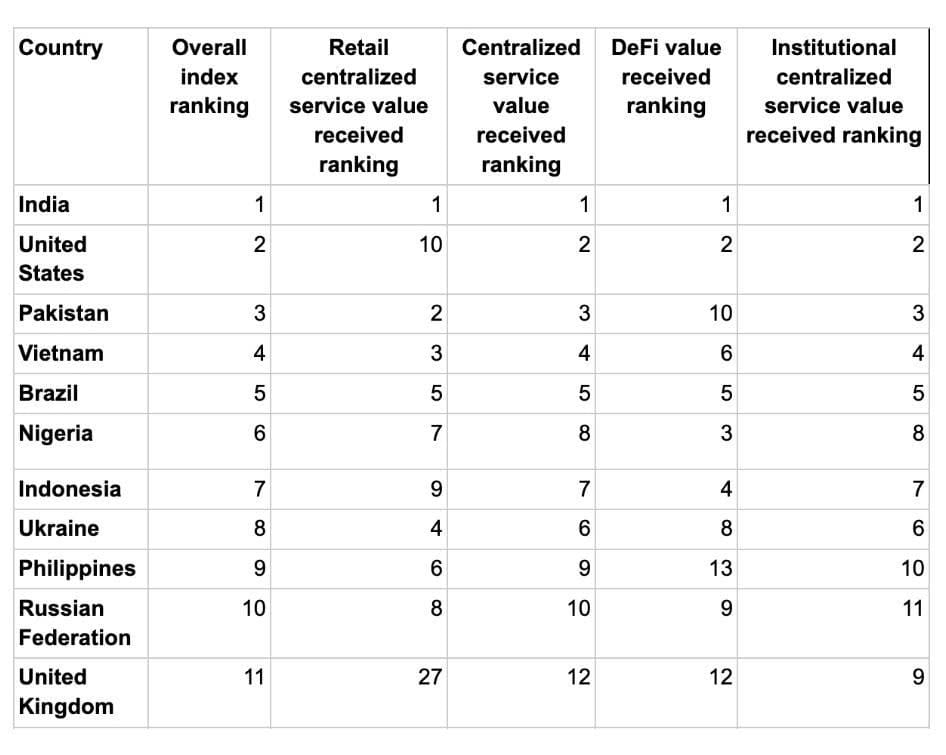
- India ranks first, leading across retail, DeFi, and institutional adoption.
- The United States ranks second, supported by ETF approvals, regulatory clarity, and strong institutional participation.
- Pakistan, Vietnam, and Brazil follow closely, highlighting the leadership of APAC and LATAM in grassroots adoption.
These figures reveal a fundamental paradox: global adoption is accelerating, yet enterprise capital is still deployed using settlement models designed for a pre-digital economy.
Why Trapped Cash Exists in Cross-Border Settlement
If the digital economy operates twenty-four hours a day, why are enterprise settlement systems still constrained by traditional business hours?
The gap is not primarily about transaction speed.
It is about capital efficiency.
In traditional cross-border payment corridors, enterprises continue to rely on pre-funding models. Capital is deposited in advance, settlements follow T+2 cycles, and large balances remain idle as trapped cash, held solely to prevent payment disruptions. Working capital is locked before any real economic value is created.
In an always-on economy, the opportunity cost of this inefficiency is significant.
This is the structural origin of trapped cash.
How Stablecoins Enable Just-in-Time Liquidity
The core issue is not how fast money moves.
It is when capital is deployed relative to when value is created.
Stablecoin-based models reverse this logic through atomic settlement.
Instead of transferring funds ahead of delivery, capital is released only when a transaction is triggered, such as when goods leave the warehouse, services are delivered, or contractual conditions are fulfilled.

This shift introduces two strategic outcomes.
- First, it removes the need for pre-funding and reduces reliance on intermediary banks within the payment chain.
- Second, it frees working capital, allowing CFOs to allocate liquidity more flexibly across core business activities.
In this framework, speed is a secondary effect.
The more meaningful metric is Liquidity Efficiency, which measures how effectively an enterprise optimizes each unit of capital instead of allowing funds to remain idle in reconciliation accounts.
This transition does not require enterprises to understand blockchain mechanics in depth. What matters is recognizing a new operational reality. Payments have become a liquidity management instrument rather than a back-office administrative step at the end of a transaction lifecycle.
For a broader perspective on this shift, see:
Why Stablecoin Rails Are Emerging as Key Infrastructure for Cross-Border Payments in 2026
The next question is no longer whether Just-in-Time Liquidity is feasible.
The real question is how enterprises can implement this model while preserving control, authorization, and compliance at an enterprise level.
This is where governance and wallet infrastructure become decisive.
Why Governance Matters More Than Speed in Enterprise Stablecoin Adoption
Just-in-Time Liquidity only delivers value when enterprises trust that cash flows remain fully controlled in real time. This is where many CFOs begin to exercise caution.
As liquidity becomes more flexible, operational risk increases in the absence of proper governance mechanisms. A system that enables instant fund movement without clear authorization and role-based controls quickly becomes a liability rather than a strategic advantage.
The critical questions are not whether stablecoins should be used, but who has signing authority, under which rules, and how human risk is mitigated.
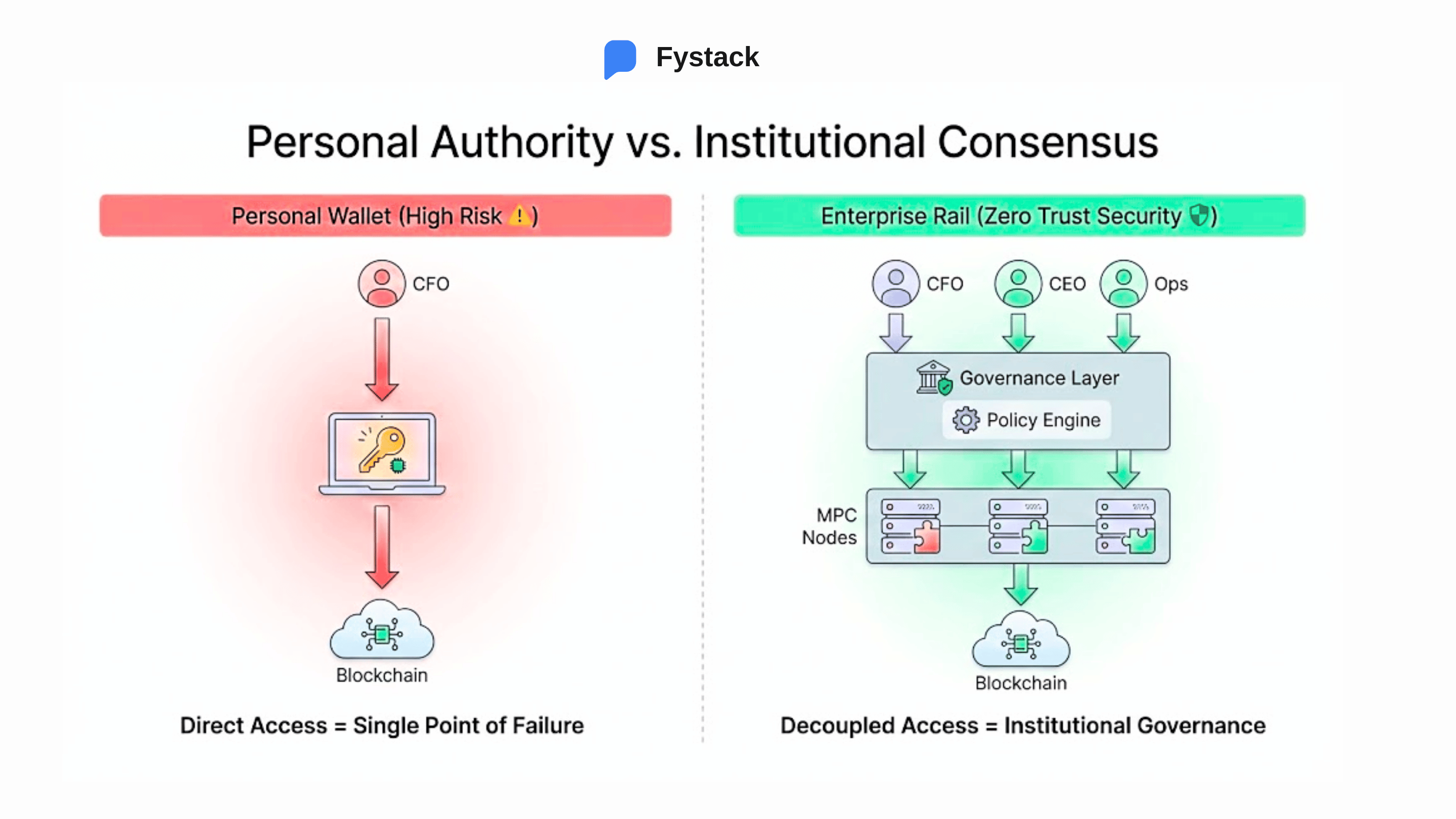
The Risk of Personal Wallets for Corporate Funds
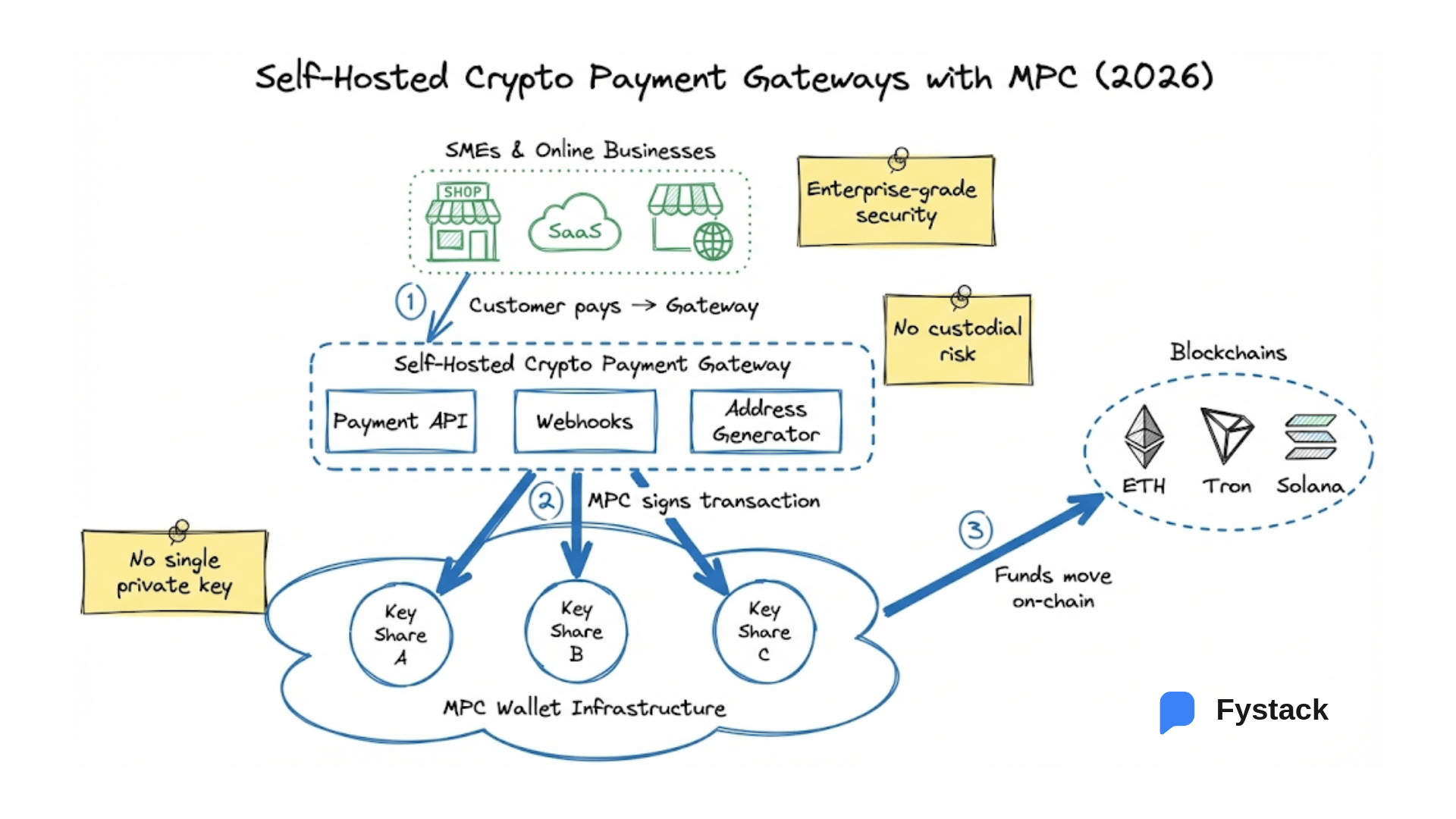
This is why enterprises cannot and should not manage corporate funds using personal wallets. The single private key model introduces an unacceptable single point of failure. A mistake, fraudulent action, or the departure of a key employee can disrupt the entire liquidity operation.
At the enterprise level, the primary challenge is not blockchain technology.
It is governance.
MPC Wallets: The Essential Governance Layer for Enterprises
MPC wallets (Multi-Party Computation wallets) address this challenge by redesigning control, not simply by securing private keys.
Instead of entrusting a private key to one individual, MPC wallets distribute signing authority across multiple parties and require collective approval before funds are released. In practice, the wallet evolves into a digital vault governed by clearly defined authorization workflows.

This allows enterprises to:
- Enforce segregation of duties in on-chain environments
- Eliminate dependency on a single individual
- Implement internal controls aligned with traditional financial governance standards
More importantly, MPC wallet infrastructure transforms Just-in-Time Liquidity from a technical capability into a model that is auditable, governable, and compliant. Liquidity is not only fast. It is released by the right stakeholders, through defined processes, and with appropriate authority.
For this reason, MPC wallets are not an optional security enhancement.
They are a mandatory governance layer for enterprises moving from periodic settlement to real-time liquidity.
For a deeper technical discussion on how MPC wallets protect private keys and enforce enterprise-grade transaction control, see:
Institutional Digital Asset Custody powered by MPC wallet: A Secure and Compliant Transaction Workflow
Real-World Case Studies: How Enterprises Actually Move Money
Stablecoins only become infrastructure when they solve concrete operational bottlenecks in enterprise finance. The following examples from Southeast Asia reveal a consistent pattern. These companies are not changing the currency they use. They are changing the logic of cash flow execution.
Hybrid Stablecoin Settlement in Southeast Asia
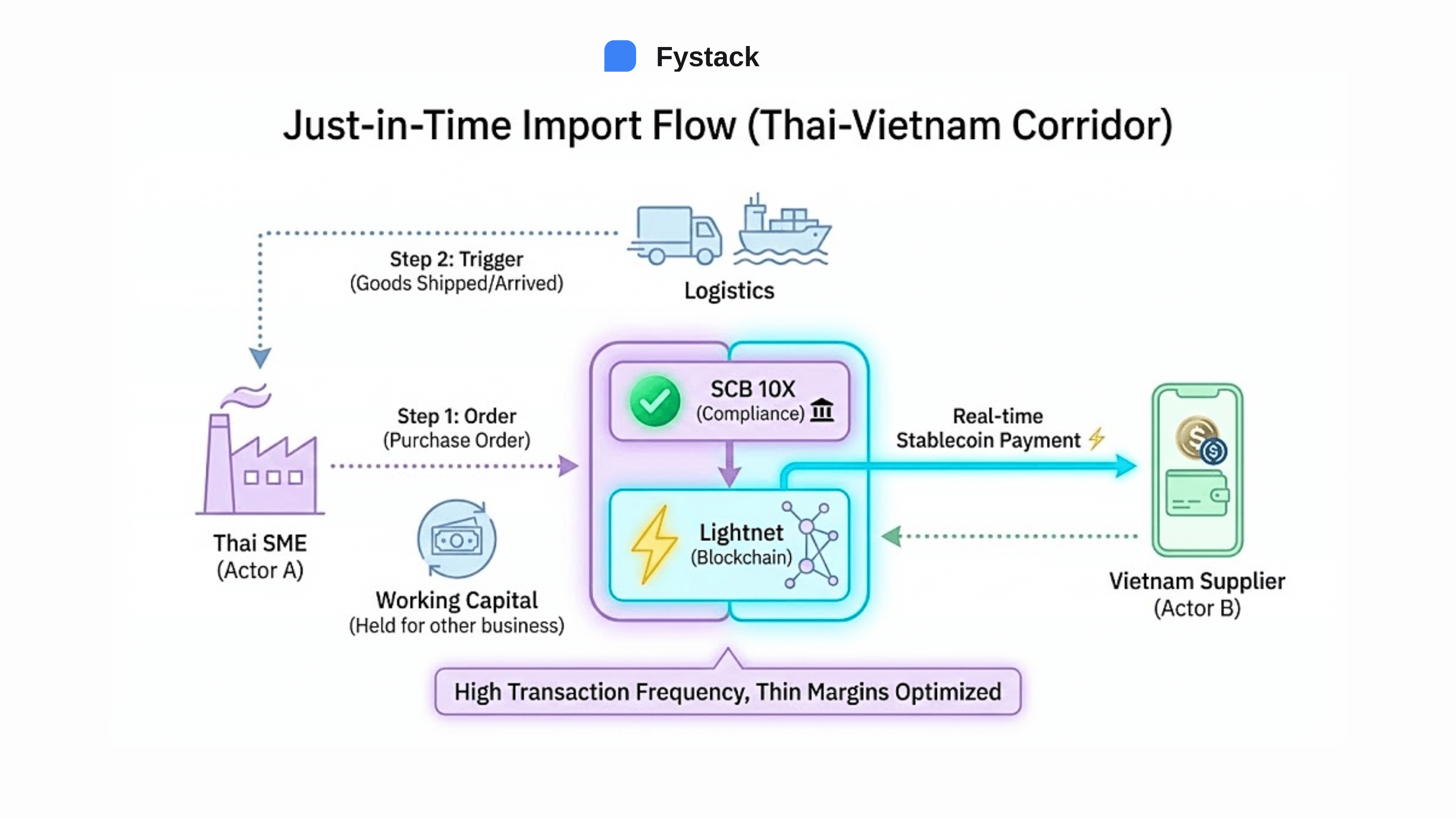
Consider Thai SMEs importing raw materials from China or Vietnam. Under traditional models, CFOs are required to pre-fund payments via SWIFT several days in advance to ensure on-time delivery. As a result, working capital is immobilized in intermediary accounts that are both inefficient and operationally risky.
The collaboration between SCB 10X and Lightnet fundamentally reshaped this model. By using stablecoins as an instant settlement layer on high-performance blockchains, while banks continue to serve as the regulatory and compliance gateway, a hybrid settlement architecture emerged.
In this model, funds are released only when the underlying commercial transaction is triggered. This is particularly impactful for trade with Vietnam, which ranks among the top global markets for crypto adoption. For SMEs operating on thin margins but high transaction frequency, this approach unlocks working capital that was previously trapped in low-yield payment corridors.
On-Chain FX and Liquidity Management for Enterprises

In Singapore and Malaysia, the use case centers on foreign exchange management. Historically, bank FX spreads were treated as a passive and opaque cost of doing business.
Initiatives such as Project Guardian are changing this perspective. By using local currency-backed stablecoins such as XSGD, enterprises gain direct access to on-chain liquidity pools. Exchange rates are transparent prior to execution and available on a continuous basis.
In this environment, foreign exchange shifts from a hidden cost to an active liquidity management instrument. Enterprises can reduce margin leakage on cross-border flows while maintaining real-time visibility over currency exposure. This capability becomes increasingly valuable when integrated into enterprise crypto wallet infrastructure governed by MPC wallets.
Programmable Payments in Logistics and Trade Finance

In Indonesia, the core challenge in the logistics sector is not capital availability, but operational trust. Maritime logistics providers often wait weeks for manual document reconciliation before receiving payment.
Programmable payments address this bottleneck by binding payment execution directly to real-world data. Instead of relying on manual approval, smart contracts automatically trigger settlement when GPS systems confirm that a vessel has arrived at port.
This model shortens the cash conversion cycle and removes entire layers of manual reconciliation. Trust shifts from human discretion to system-level enforcement, embedded directly within the payment infrastructure.
Settlement as a Liquidity Decision for CFOs
Across these markets, one pattern is consistent. Stablecoins are applied where capital has historically been locked for the longest time, not where payments are merely slow.
When funds are released exactly at the moment economic activity occurs, enterprises reduce two costs at the same time: operational risk and the cost of idle capital. Cash is no longer parked in advance to absorb settlement delays. It is deployed only when value is created.
From a CFO’s perspective, this is no longer a technology upgrade. It is a change in how liquidity is planned, controlled, and deployed in an always-on economy.
As enterprises scale this model, a new constraint emerges. The question is no longer how fast money can move, but how internal financial rules, approvals, and risk controls can be enforced safely in real time on-chain.
That question leads directly to the next layer of value.
Beyond Settlement: How Enterprise MPC Wallets Create CFO-Level Value
Once payment speed is no longer a constraint, the next question a seasoned CFO will ask is more fundamental.
If money can move this fast, how do we control it, and how does finance keep pace?
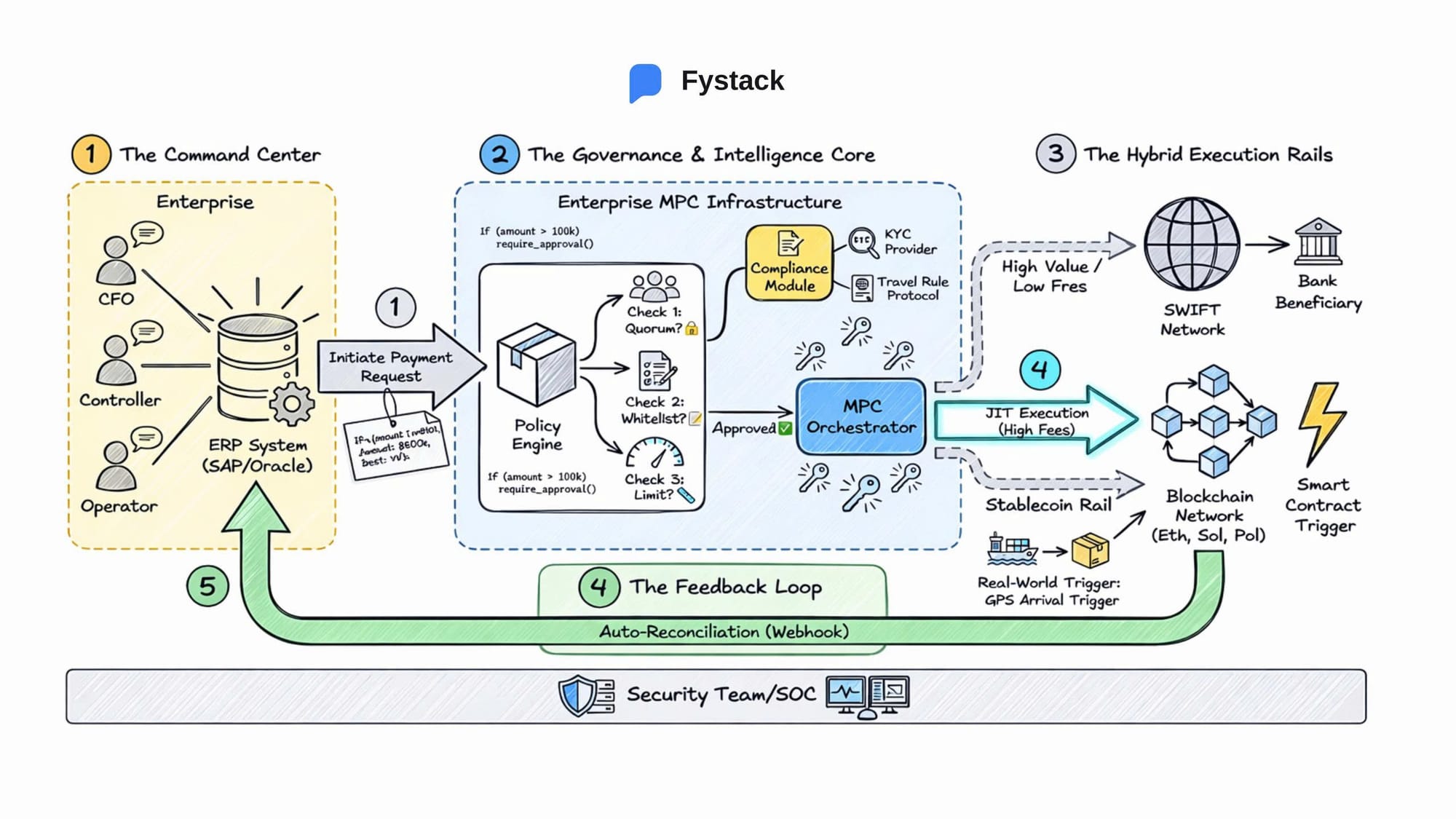
The true enterprise value of stablecoins does not reside solely in the settlement layer. It emerges at the two layers above it: governance and integration. This is where MPC wallet infrastructure evolves from a security tool into a core component of corporate treasury architecture.
Automating Financial Controls with MPC Policy Engines
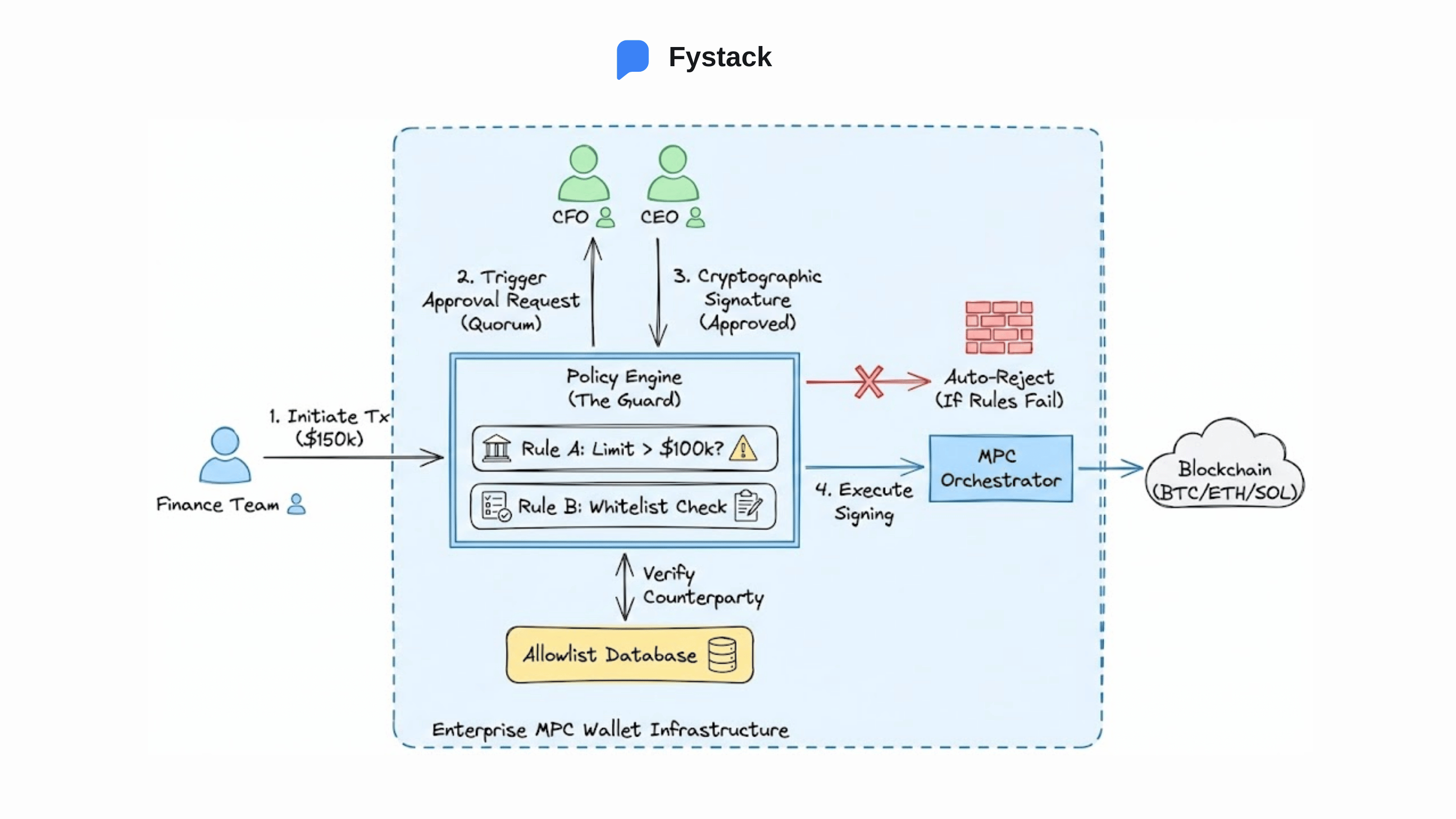
In traditional finance, compliance relies on human adherence to rules.
In on-chain systems, those rules can be enforced directly through code.
This is the role of the Policy Engine within an enterprise MPC wallet.
Instead of relying on trust between individuals, enterprises encode financial policies directly into wallet infrastructure.
Examples include:
- Quorum-based approvals
A transfer exceeding USD 100,000 may require multiple approvals, such as initiation by the finance team, authorization by the CFO, and final approval by the CEO. - Spending limits and whitelists
A marketing wallet can be assigned a fixed monthly budget and restricted to pre-approved counterparties such as advertising platforms or SaaS vendors.
Any transaction that violates these rules is automatically rejected by the system before it reaches the blockchain.
In this model, governance is no longer an external process layered on top of payments. It is embedded directly within the execution layer through MPC wallets, reducing operational risk while preserving speed.
ERP Integration: Solving the Reconciliation Challenge
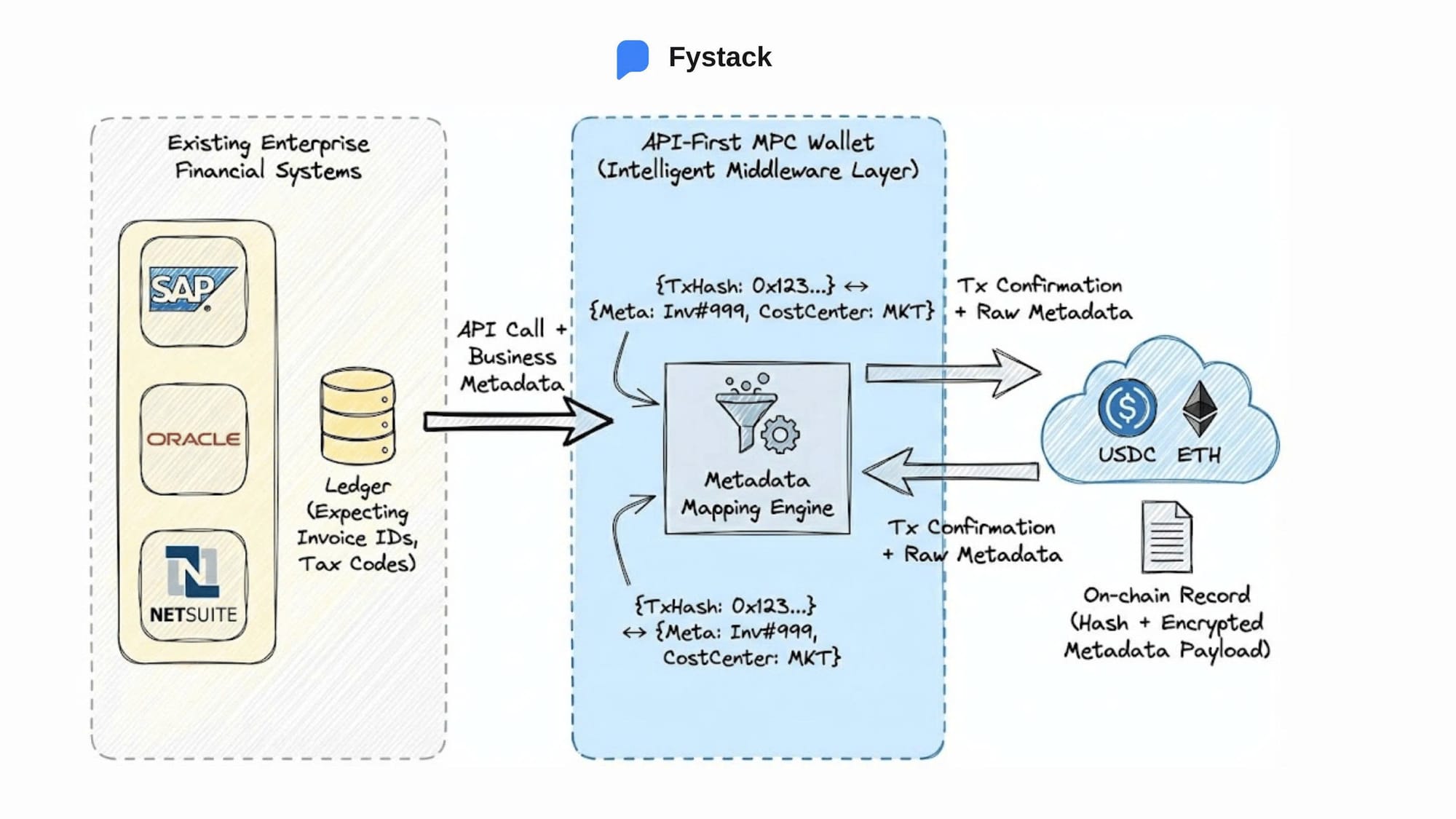
Reconciliation is often the most significant barrier to enterprise adoption.
The challenge is not executing transactions on-chain, but aligning blockchain records with internal financial systems.
How does a blockchain transaction hash map to a specific invoice inside SAP, Oracle, or NetSuite?
The answer lies in metadata.
API-First MPC Wallet Architecture for ERP Compatibility
Modern enterprise wallet infrastructure, such as MPC wallets designed for corporate use, is built with an API-first architecture. It functions as an intelligent middleware layer that directly maps on-chain metadata fields to ERP data structures.
Each on-chain transaction carries a metadata payload that can include invoice IDs, tax identifiers, cost centers, or internal reference codes.
Real-Time Reconciliation Using On-Chain Metadata
Through webhooks and real-time APIs, this data is pushed back into financial systems as transactions occur. The result is automated reconciliation.
Accounting teams no longer rely on manual data entry or post-hoc matching. Ledger entries are synchronized in real time, improving accuracy, audit readiness, and operational efficiency. Most importantly, this approach preserves compatibility with existing enterprise systems without requiring costly system replacements.
Immutable Audit Trails and Compliance in MPC Wallet Infrastructure

In enterprise environments, knowing who can move funds is important. Knowing who approved a transaction, when it was approved, and under what conditions is even more critical, especially during audit cycles.
MPC wallet infrastructure provides an immutable internal audit trail that goes beyond basic blockchain transparency.
Key characteristics include:
- Forensic-grade logging
Every action related to a wallet is permanently recorded, including transaction initiation, approval steps, and rejected access attempts. - Context-aware records
Audit logs capture not only the action but also its context. This can include device type, network location, and authentication method used during approval. - Audit-ready reporting
When auditors engage, enterprises can export structured audit logs directly, rather than reconstructing approval histories manually.
This capability shifts the role of compliance from passive oversight to proactive risk management, embedded directly into the financial infrastructure.
From Payments to PayFi: Liquidity Financing with MPC Wallets
The final evolution shaping 2026 is PayFi, or Payment Finance.
Rather than treating payments, custody, financing, and compliance as separate systems, the PayFi Stack defines how these layers must work together to support real-world enterprise use cases.
The initial PayFi Stack consists of six core layers:
- Transaction - execution of payments and settlement events
- Currency - stablecoins and tokenized money used for value transfer
- Custody - enterprise-grade wallet infrastructure, governed by MPC
- Financing - liquidity provision based on real-time transactional data
- Compliance - policy enforcement, auditability, and regulatory controls
- Application - business systems that trigger and consume PayFi flows
As adoption matures and regulatory frameworks evolve, this stack will continue to develop. But the principle remains constant: PayFi only works when financing logic, custody, and compliance are embedded directly into the payment execution layer.
This is why MPC wallet infrastructure is foundational to PayFi. It provides the governance, control, and auditability required to safely transform payment flows into financing instruments.
For a deeper breakdown of the infrastructure required to support production-grade stablecoin and PayFi systems, see: The 11 Core Components Every Production-Grade Stablecoin Rail Must Have in 2026
The Future of Enterprise MPC Wallet Infrastructure Toward 2030
Data from leading financial institutions indicates a clear transformation in wallet infrastructure. Enterprise wallets are evolving from passive storage tools into active operational layers within financial systems.
Three infrastructure trends are expected to define the next decade, reinforced by strategic industry research.
Embedded Finance and Invisible MPC Wallets
Basic custody will become a standardized utility. Competitive advantage will shift toward the ability to transform custodial assets into productive, yield-generating instruments.
According to a strategic report from Boston Consulting Group (BCG), the market for tokenized real-world assets is projected to reach USD 16 trillion by 2030. This implies that enterprises will require more than a secure place to store assets. They will need infrastructure capable of managing tokenized bonds, credit instruments, and cash equivalents directly within enterprise MPC wallets.
Why Digital Asset Custody Is Becoming a Commodity
The boundary between operational applications, such as ERP and logistics systems, and wallet infrastructure is beginning to disappear.
Bain and Company projects that embedded finance will account for approximately ten percent of total transaction value. In Web3 environments, this drives the emergence of invisible wallets, where MPC wallet functionality is deeply embedded into non-financial platforms to automate payments and financial workflows.
In this model, wallets are no longer standalone applications. They become native components of enterprise software stacks.
Compliance by Design in Enterprise Wallet Infrastructure
As regulatory frameworks such as MiCA in Europe and VARA in Dubai mature, wallet infrastructure must incorporate compliance capabilities by default.
PwC research consistently identifies regulatory uncertainty as a primary barrier to institutional adoption. As a result, RegTech modules embedded within MPC wallet infrastructure are becoming essential to unlocking institutional capital flows.
RegTech is the model of embedding regulatory compliance directly into wallet infrastructure and payment systems, allowing regulatory rules to be enforced automatically and in real time during transaction execution. In the context of MPC wallets, RegTech transforms compliance from a post-transaction review process into a core component of system architecture.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Just-in-Time Liquidity in enterprise payments?
Just-in-Time Liquidity is a payment model where capital is released exactly when economic activity occurs, rather than being pre-funded in advance. It enables enterprises to deploy working capital only at the moment value is created, significantly improving liquidity efficiency.
Why are stablecoins relevant for enterprise treasury beyond faster payments?
The strategic value of stablecoins lies in liquidity timing rather than transaction speed. Stablecoin rails eliminate pre-funding, reduce trapped cash, and allow payments to function as an active liquidity management instrument instead of a back-office settlement process.
Why are personal wallets unsuitable for managing corporate funds?
Personal wallets rely on single private keys, creating a single point of failure. They lack enterprise-grade governance such as role-based access control, approval workflows, segregation of duties, and auditable transaction histories.
How do MPC wallets act as a governance layer for enterprises?
MPC wallets distribute signing authority across multiple parties and enforce predefined approval rules before transactions are executed. This embeds governance, internal controls, and compliance directly into the payment execution layer while preserving real-time liquidity.
What is the role of RegTech in enterprise MPC wallet infrastructure?
RegTech embeds regulatory compliance directly into wallet and payment infrastructure, allowing regulatory rules to be enforced automatically and in real time. In MPC wallets, RegTech transforms compliance from a post-transaction review into a core architectural component.
Conclusion
Market projections estimate that digital asset custody could reach USD 3 trillion in assets under custody by 2032. This figure defines the scale of the opportunity.
In this future, a wallet is not merely a place to store funds.
It functions as a programmable financial institution.
Whoever controls wallet infrastructure controls the first point of interaction with cash flows. Whoever controls wallet infrastructure controls the enterprise relationship.
For enterprises in Southeast Asia, the strategic question today is not whether stablecoins should be used. The real question is whether existing financial infrastructure is flexible enough to participate in a USD 3 trillion digital asset economy.
At Fystack, we are building the infrastructure to help enterprises answer that question with confidence.
If you care about security, compliance, and reliability in Web3 operations:
👉 Try Fystack today: https://app.fystack.io
👉 Join our Telegram community for web3 security updates, engineering insights & product updates: https://t.me/+9AtC0z8sS79iZjFl