Top Crypto Hacks of 2025: Why We Still Fail to Protect Digital Assets
Phoebe Duong
Author

2025 isn’t just the year DeFi makes its comeback - it’s also the year blockchain hacks return stronger than ever. You might be using a self-custody wallet, staking your favorite token, or have just deployed a smart contract - yet somewhere, a single line of code is waiting to be exploited.
If you’ve ever wondered:
- Which blockchains suffered the most breaches this year?
- Why do supposedly “decentralized and fully secure” wallets still get drained overnight?
- And what exactly turned 2025 into the most chaotic year for Web3 security?
Then this is the deep-dive you’ve been looking for.
Using verified data from CertiK and Chainalysis, this article breaks down the key attack vectors, real-world cases, and the technical and human flaws behind 2025’s biggest Web3 hacks - helping builders and teams strengthen their digital asset security posture.
From a security infrastructure perspective, 2025 marks a pivotal evolution in how Web3 custody is designed. The conversation is no longer just about “smart contract audits” or “cold storage.” It’s about operational resilience, key management, and human governance - the invisible layers that decide whether billions stay protected or vanish overnight.
If you want to dive deeper into the Solana hacks of 2025, including how meme tokens and hot wallets were drained in seconds, check out Protect Your Solana Memecoins: Shield Against 2025 Hacks with MPC Wallets.
The Real Attack Surface: Why We Still Fail to Protect Digital Assets
According to CertiK’s latest 2025 Hack3d Report, 69% of total losses in the first half of the year came from wallet compromise - poor key management and hot wallet operations, not blockchain protocol exploits. Another 17% resulted from phishing and social engineering, 11% from smart contract vulnerabilities, 2% from weak access control, and less than 1% from oracle or data manipulation attacks.
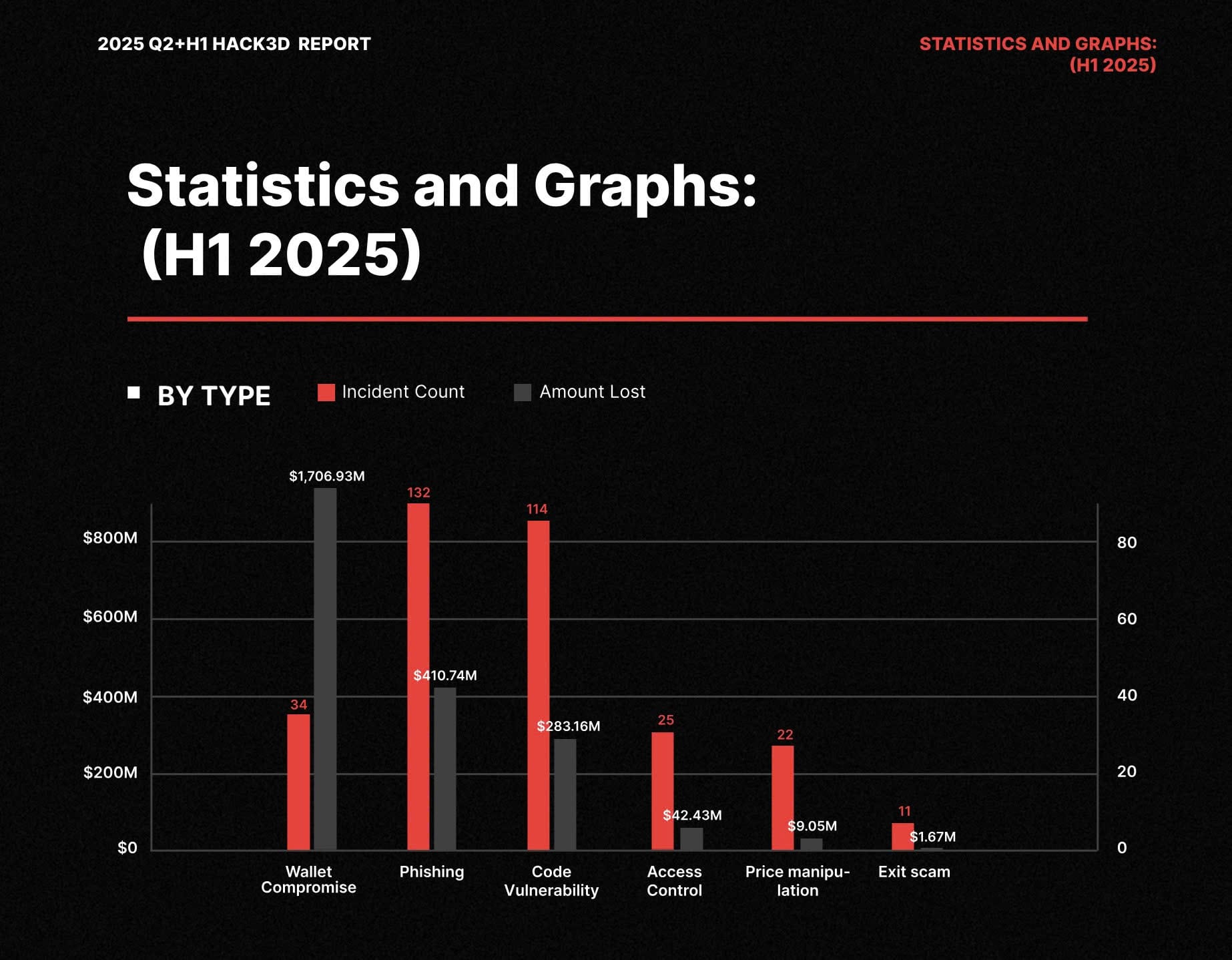
These numbers reveal an uncomfortable truth:
The majority of crypto losses don’t come from blockchain failures - they come from how we, humans, build and operate around it.
While blockchain infrastructure keeps evolving, our digital asset security awareness and operational discipline haven’t caught up. We’re trying to protect decentralized assets with centralized mindsets - inherited from Web2, where single admin control, manual approval, and human error remain the weakest links in the system.
From a custody engineering standpoint, the real attack surface in 2025 lies not in code, but in governance, access control, and trust design. As Web3 matures, the question shifts from “Is the blockchain secure?” to “Can your operations survive a single compromised key?”
1. Wallet Compromise - The $1.5B Lesson from Bybit
On February 21, 2025, Bybit suffered one of the largest crypto heists in history, with approximately $1.5 billion (401,000 ETH and stETH) drained from an ETH multisig cold wallet due to a sophisticated attack by the North Korean Lazarus Group.
This was not a smart contract bug or bridge exploit but a targeted supply chain attack exploiting the user interface (UI) of Safe{Wallet}, Bybit’s multisig wallet provider.
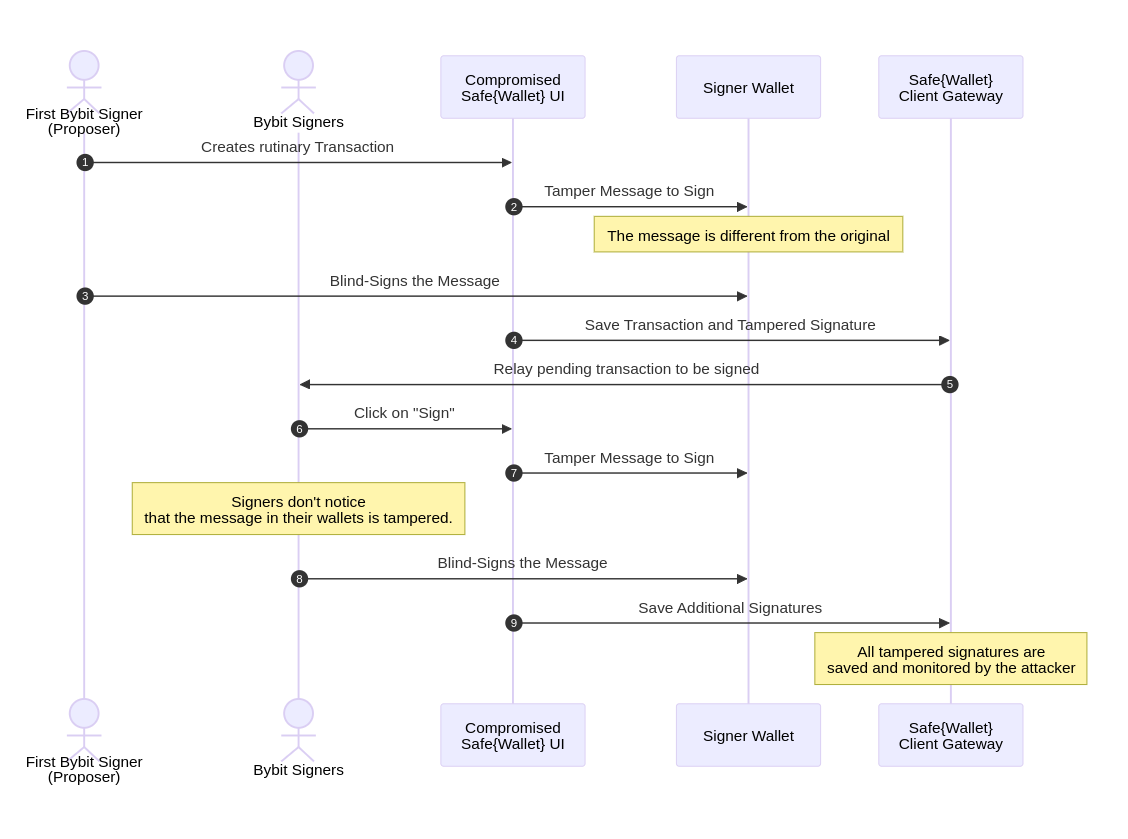
Malicious JavaScript injected into the UI tricked multiple signers, including the CEO, into approving a routine transfer, allowing hackers to manipulate the underlying smart contract logic and siphon funds.
This wasn’t just a coding issue - it was a governance failure.
Despite using a cold multisig wallet requiring at least three signers, Bybit’s reliance on a third-party UI introduced a critical vulnerability. The incident highlights that even robust setups like multisig can fail without rigorous auditing of off-chain components and real-time monitoring.
Many exchanges and DeFi protocols use cold wallets for security, but vulnerabilities in signing processes or external tools can turn safeguards into liabilities.
A single phishing attempt, compromised endpoint, or malicious UI update can lead to catastrophic losses.
The takeaway is clear: Security doesn’t come from self-custody alone - it comes from structured custody.
Modern frameworks like MPC (Multi-Party Computation) and enhanced multisig architectures are redefining digital asset custody.
By distributing signing power, enforcing withdrawal limits, and maintaining audited workflows, these systems eliminate single points of failure inherent in traditional setups.
Learn more: MPC vs. Multisig Wallets
From a security perspective, this shift marks a pivotal evolution in Web3 custody-moving away from trust-based control toward cryptographic collaboration.
2. Phishing & Social Engineering - The Human Layer of Failure
If Bybit’s breach was a wake-up call for institutions, then EtherHiding and Solflare served as sharp reminders for everyday users.
The EtherHiding campaign, linked to North Korea’s UNC5142 group, compromised over 14,000 WordPress websites by exploiting plugin vulnerabilities. Malicious JavaScript was injected to hide payloads within smart contracts on BNB Smart Chain.
"UNC5142 is characterized by its use of compromised WordPress websites and 'EtherHiding,' a technique used to obscure malicious code or data by placing it on a public blockchain, such as the BNB Smart Chain," Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG) said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
These scripts lured users into connecting wallets through fake updates or drive-by downloads, leading to credential theft and crypto drains via info-stealers such as Atomic and Lumma.
On Solana, hundreds of Solflare users also fell victim to near-perfect phishing clones (e.g., solfllare.live), often promoted via Discord or Telegram using airdrop bait, resulting in seed phrase theft and wallet drains - with isolated cases losing up to 60 SOL or $115 worth of NFTs.
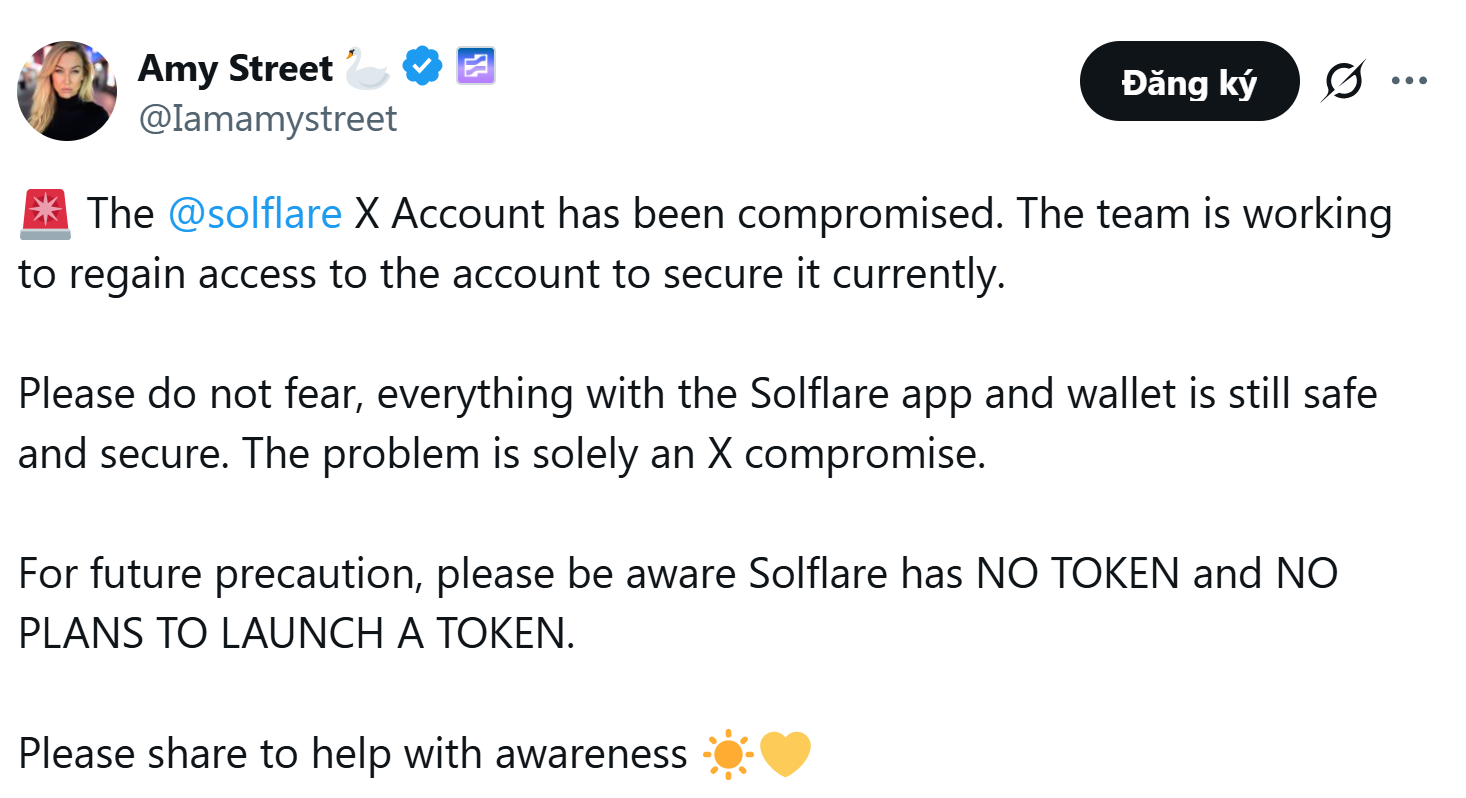
According to Chainalysis, phishing and related attacks caused $2.17 billion in total losses from crypto services in H1 2025, marking a 17% increase over H1 2022 - the previous record half-year for crypto thefts.
The shocking part? No blockchain code was ever broken.
Every loss originated from human behavior - users skipping domain verification, trusting familiar-looking interfaces, and signing transactions without reviewing details.
We’ve grown too comfortable with seamless UX, overlooking red flags like mismatched URLs or unsolicited pop-ups.
“Knowing how to use a wallet” isn’t the same as “knowing how to protect one.”
Basic security habits - such as verifying domain integrity (e.g., bookmarking solflare.com), checking contract addresses, and using wallets with built-in scam blockers or transaction previews - must become instinctive.
As discussed in Security 101 for Web3 Startups, decentralized systems still require structured governance, not less control, but smarter control.
3. Smart Contract Bugs - Code Doesn’t Fail, Process Does
In the first half of 2025, smart contract vulnerabilities accounted for about 8% of total crypto losses - roughly $263 million out of $3.1 billion.
Most of these incidents stemmed from logic flaws in reused libraries or insufficient post-audit testing. (Source: cointelegraph)
The Cetus Protocol exploit ($223 million) was a prime example: an arithmetic overflow bug in a shared math library (written in Move) allowed attackers to inject spoof tokens, manipulate liquidity parameters, and drain multiple pools on the Sui blockchain in under 15 minutes.
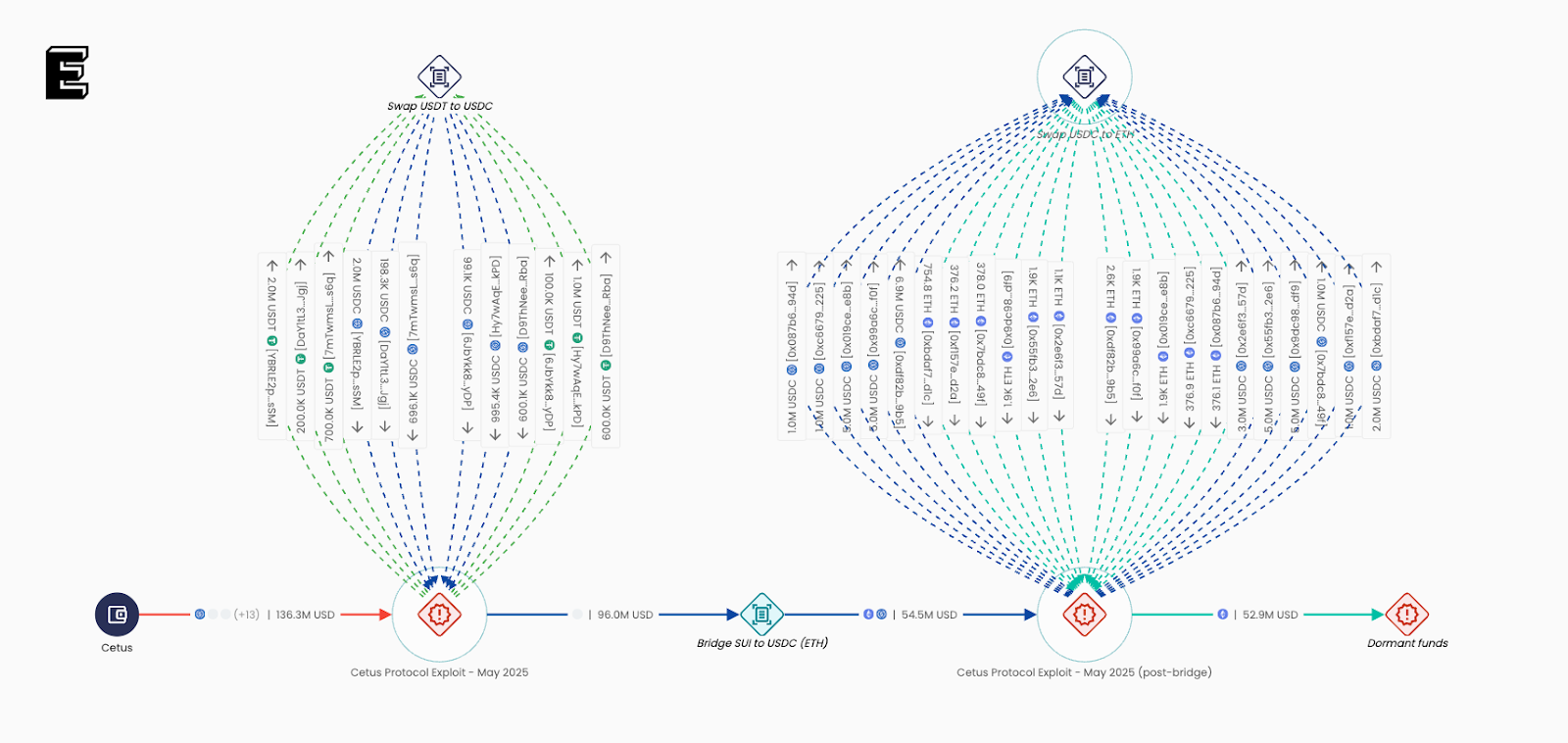
The issue wasn’t the programming language - whether Solidity, Move, or Rust - but the development and audit process itself. Too many teams treat audits as the end of security, when in reality, they’re only the beginning.
A contract that is secure today can become vulnerable after a minor upgrade, fork, or new integration, as exploit chains often combine code-level flaws with operational oversights.
The lesson: Security isn’t about “passing the audit.” It’s about continuous testing, monitoring, and lifecycle governance.
Projects should integrate automated fuzzing tools, timelocks before upgrades, and emergency pause mechanisms for high-TVL pools - just as Cetus did to freeze $162 million mid-exploit.
From a security infrastructure perspective, this marks a pivotal evolution in how Web3 smart contract management should be designed - shifting from one-time audits to continuous assurance frameworks.
For a concise security checklist for Web3 startups, see Security 101 for Web3 Startups.
4. Access Control - Small Teams, Big Risks
Approximately 1.7% of confirmed Web3 losses in the first half of 2025 (around $42.43 million out of $2.455 billion, according to CertiK’s H1 Hack3d Report) originated from internal governance failures, such as weak access control.
However, broader industry data from Hacken suggests a much larger impact - roughly 25% of total losses (~$775 million out of $3.1 billion) -with smaller teams hit the hardest due to limited operational resources.
Many projects still rely on a single admin wallet with no key rotation, no multi-role authorization, and no transaction approval workflow. Both 0xInfini and ALEX Lab suffered severe losses from access control flaws:
- 0xInfini lost $49.5 million USDC (February 2025) after a former developer exploited retained admin privileges,
- ALEX Lab lost $8.3 million (June 2025) due to a self-listing verification flaw that granted unauthorized vault access.
These incidents expose a common misconception - confusing decentralization with disorganization.
Regardless of project size, internal governance remains the backbone of digital asset security. Mechanisms like multi-signature approvals, transaction limits, and real-time security alerts can be implemented through modern APIs or wallet providers - often at minimal cost (~$1K–5K).
Another critical layer in access control security lies in encryption and key management. The DEK–KEK (Data Encryption Key – Key Encryption Key) model is rapidly becoming the industry standard for protecting highly sensitive data and private keys - mitigating risks tied to poor access control and phishing vectors alike.
Learn more: DEK–KEK: The Industry Standard to Protect Highly Sensitive Data (Fystack)
From a Web3 security architecture perspective, the real evolution now is toward programmable access control - where operational safety is built into the code, not dependent on human discipline.
5. Oracle & Data Manipulation - When Speed Outpaces Control
Though oracle attacks accounted for less than 1% of total losses in 2025, they remain powerful examples of the limits of real-time blockchain systems.
In the Phemex exploit ($73 million), attackers exploited a brief delay in oracle price updates to manipulate liquidation logic within seconds - draining assets before human monitors could even react.
When blockchain transaction speed surpasses human oversight capacity, “instant” response may already be too late.
The lesson is clear: speed must come with control. Oracle systems must integrate multi-source price feeds, enforce sanity checks, and deploy automatic circuit breakers to halt abnormal transactions when volatility spikes.
In this context, real-time monitoring across both custody layers and DeFi infrastructure has become more critical than ever. Platforms like Fystack now enable instant visibility into deposits, withdrawals, approvals, and balance changes - with real-time alerts via Telegram or Slack, allowing operations teams to respond immediately to anomalies rather than discovering them after losses occur.
Read more: Advanced Monitoring for MPC Wallets – Get Instant Telegram & Slack Alerts for Deposits, Withdrawals, Approvals, and Balance Thresholds
Lessons for Builders: The Shift to MPC & Secure Governance
After a wave of high-profile exploits, one truth has become clear:
Web3 security is no longer about having a private key - it’s about how that key is shared, managed, and governed.
From Bybit to ALEX Lab, every major breach exposed the same weak point: a single point of control. That’s why, in 2025, more institutions have begun migrating toward MPC (Multi-Party Computation) - the natural next step in decentralized custody.

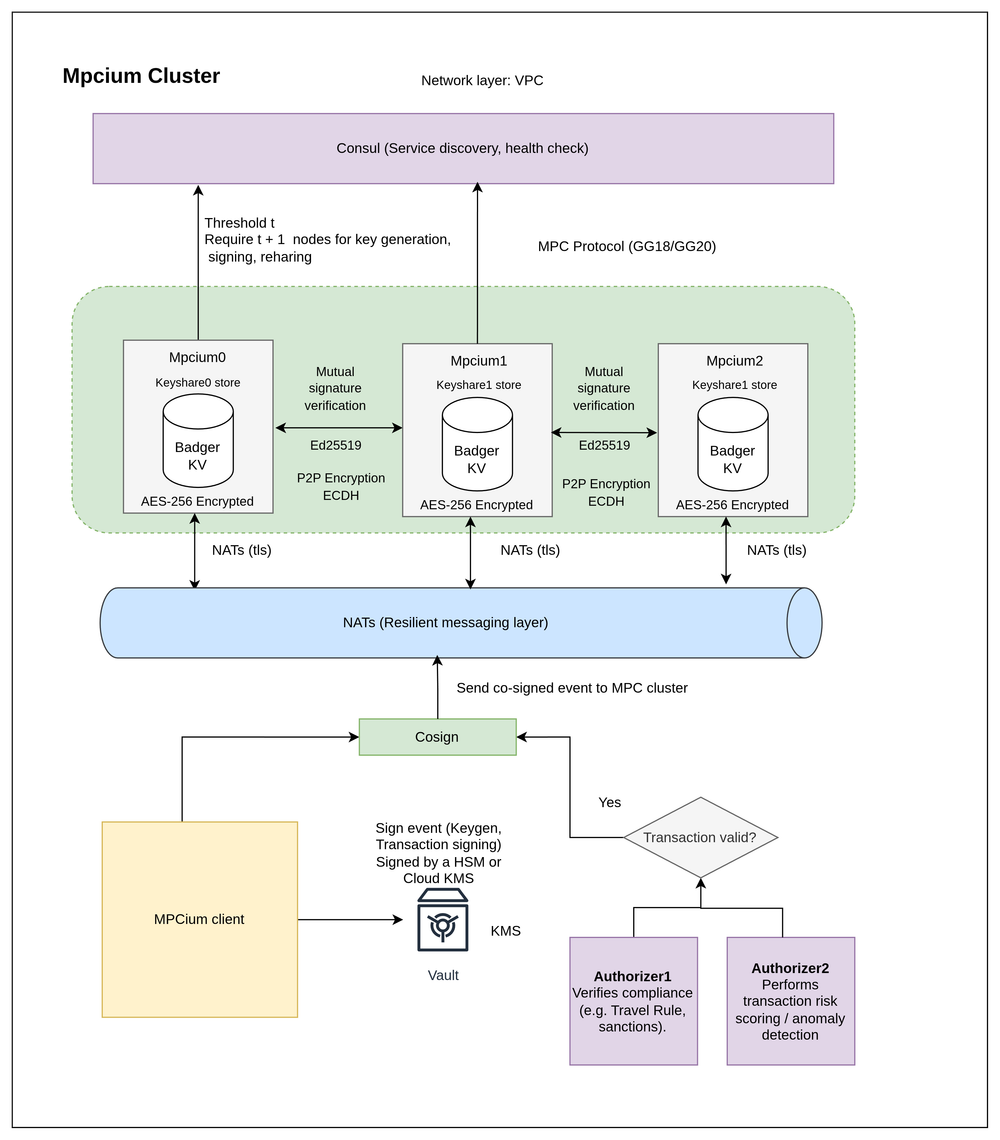
1. MPC – Security Built on Math, Not Trust
In traditional wallet architectures, a private key exists in one complete form - whoever holds it, controls the funds. MPC changes that paradigm. It splits the private key into multiple key shares, distributed across independent nodes or devices. No single party - not even the admin - ever possesses the full key.
When a transaction is initiated, multiple parties jointly compute a cryptographic function to generate a valid signature without ever reconstructing the key.
This architecture brings three foundational advantages:
- No single point of failure: An attacker can’t drain funds by compromising one device or account.
- True decentralization: Organizations can require multi-party approvals, automate withdrawal limits, and enforce on-chain policies.
- Frictionless experience: For end users, the flow feels as seamless as a standard wallet - the difference lies in invisible, mathematically enforced security beneath the surface.
From a security infrastructure perspective, this marks a pivotal evolution in how Web3 custody is designed - moving from “keep your key safe” to “design your system so no one can lose it.”
2. From Trust-Based to Code-Based Control
Legacy operations rely heavily on human trust: We trust that admins won’t make mistakes, developers won’t leak keys, and auditors will catch every bug. MPC redefines that foundation - replacing human trust with coded policy.
Learn more: MPC vs. Multisig Wallets
Instead of assuming someone won’t mis-sign, we encode the rules directly into logic:
- Transactions exceeding a limit require multi-party authorization.
- Withdrawals are time-locked before execution.
- Every action is logged, versioned, and auditable in real time.
When authority is expressed in code, humans stop being the weakest link.
As security engineers across Web3 infrastructure teams emphasize:
“Governance isn’t about who you trust - it’s about how you codify trustlessness.”
This shift is restoring blockchain’s original ethos: transparent, decentralized, and verifiable control.
3. MPC Is Not Just Technology - It’s Governance Reimagined
Adopting MPC isn’t merely a technical upgrade; it forces teams to rethink their entire operational governance model. Who signs? How are approvals structured? What happens when one party is compromised?
Answering these questions demands structured workflows where every action follows a policy, and every policy has built-in safeguards.
That’s why leading enterprises, funds, and wallet infrastructure providers like Fystack are going MPC-native:
- Distributing signing authority to minimize internal risk.
- Maintaining transaction speed and UX parity for end users.
- Integrating audit logs, timelocks, and policy engines into one unified framework.
In essence, MPC unites security and efficiency - blending cryptographic assurance with operational discipline.
Conclusion
The events of 2025 are not the end of trust in Web3 - they are its maturation point. Blockchain technology has proven resilient, but only when combined with modern security practices, process discipline, and cryptographic governance can the ecosystem reach true safety.
MPC is not a silver bullet against hacks - it’s the starting point of a new operational model, where power is distributed, responsibility is codified, and digital assets are protected by mathematics, not promises.
If you’re still exploring whether MPC infrastructure is the right fit for your organization, we’d love to continue the conversation. Join the discussion on our Telegram group to connect directly with Fystack engineers and builders.