MPC vs. Multisig Wallets
Kristie Le
Author

In the world of digital assets, private keys define ownership. Whoever controls the key controls the asset.
As crypto adoption moves beyond individuals into companies, fintechs, and payment platforms, the limitations of single private keys become clear. Organizations now require secure, scalable, and policy driven approaches to crypto key management.
Two technologies dominate this discussion today: Multi Party Computation (MPC) wallets and Multi Signature (multisig) wallets. Both aim to remove the single point of failure in private key management, but they differ significantly in security architecture, operational flexibility, and enterprise readiness.
Quick Look: The Evolution of Crypto Key Management

Before diving in, let’s take a quick tour of how key management has evolved:
- Single private key: One wallet, one private key. Simple, but creates a single point of failure: if the key is lost, stolen, or misused, the funds are gone.
- Multisig wallets: Introduced better protection. Multiple independent keys must sign a transaction. Safer, but not always flexible.
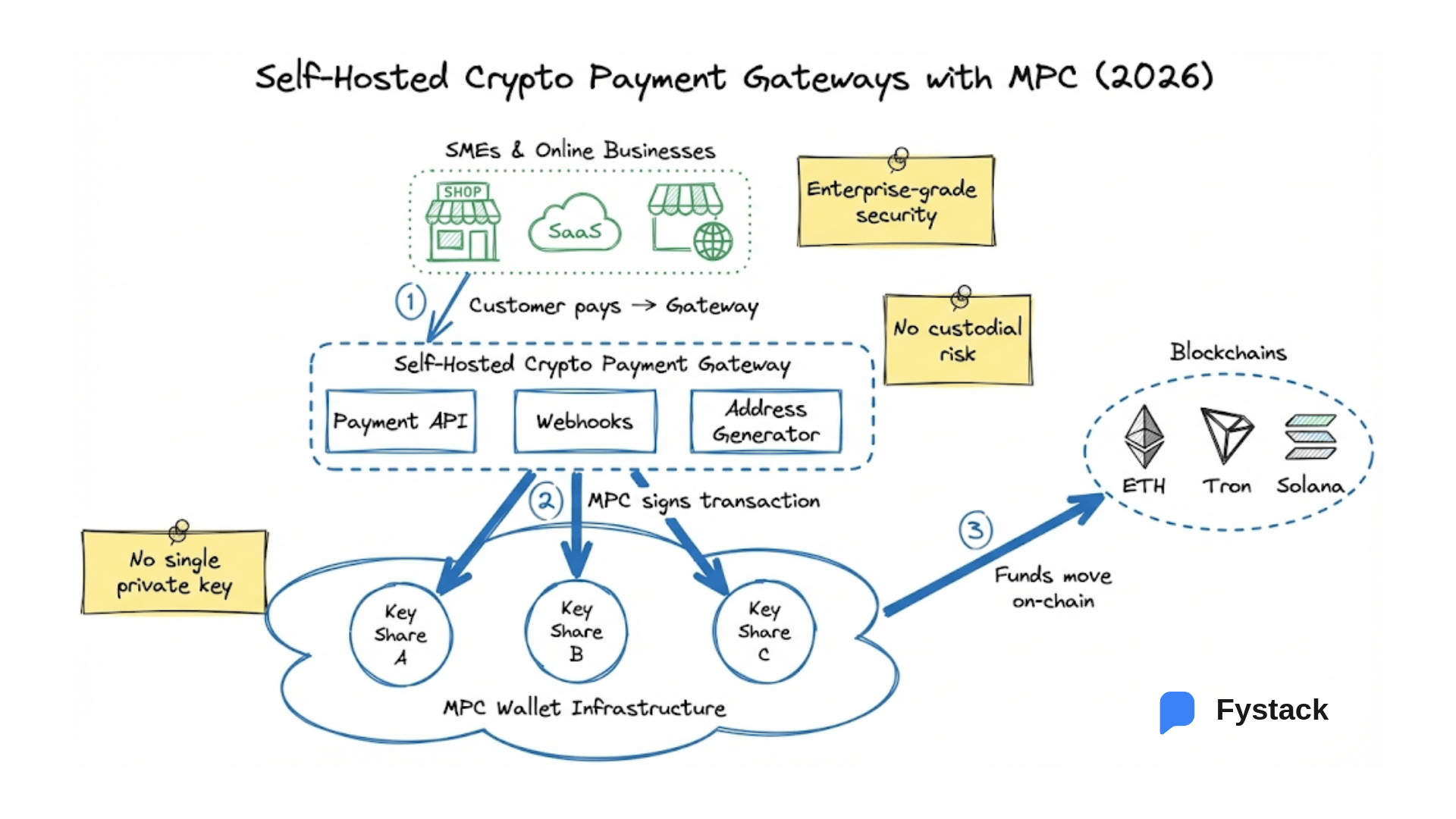
- MPC wallets: The latest approach. The private key is never created in full. Instead, it’s split into pieces (shares), and signing is done collectively.
This shift reflects the growing demand for stronger security, better team collaboration, and more flexible wallet operations.
Why MPC Wallets Are Becoming the Enterprise Standard in 2026
By 2026, crypto wallets are no longer just storage tools. For enterprises, wallets have become execution infrastructure for payments, treasury, and cross chain operations.
This shift changes the evaluation criteria. Security alone is not enough. Enterprises now care about operational continuity, governance flexibility, compliance readiness, and long term maintainability.
In this context, MPC wallets are increasingly adopted not just as a security upgrade, but as a foundational layer for enterprise crypto operations.
What Is Multi-Signature (Multi-Sig)?
Multisig stands for multi-signature. In this model, a wallet is configured to require signatures from multiple private keys before a transaction is approved.

Think of a multisig wallet like a bank vault that requires multiple keys to open. Instead of just one person having full control, several authorized individuals each hold their own key, and a subset of them must approve any transaction.
How it works:
- A wallet is configured with multiple private keys (e.g., five).
- A rule is set for how many signatures are needed to approve a transaction (e.g., 3-of-5).
- Each signer uses their individual private key to approve the transaction.
- Once the threshold is met, the transaction is processed.
Why Companies Use It:
- Reduces risk of a single compromised device.
- Helps with internal controls: finance teams, compliance leads, and executives can share responsibility.
- Proven model for crypto treasury management, especially on Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Limitations:
- Not all blockchains support native multisig (e.g., Solana or some L2s).
- The configuration is hardcoded. If someone leaves the team or the business structure changes, updating the wallet can introduce complications or mean setting up a new one.
- Each key is a full private key. If one is compromised, it's still a risk.
That lack of flexibility can become a real issue for growing teams. Say a company hires a new CFO or restructures its leadership. Updating a multi-sig wallet would often mean creating a new wallet or redeploying a smart contract. This process can interrupt operations or increase security risk during the transition.
This inflexibility is especially challenging for companies still evolving their org structure or needing agility. That’s where MPC comes in.
What Is Multi-Party Computation (MPC)?
MPC, or Multi-Party Computation, is a cryptographic technique where a private key is never created or stored in full. Instead, it is broken into key shares held by multiple parties, devices, or environments. The transaction is signed collectively, without ever reconstructing the original key.
Imagine a vault code split across three managers. None of them ever see the full code, but when they each input their part, the vault opens.
Why It’s Gaining Adoption:
- Chain-agnostic: Works with any blockchain.
- Privacy-preserving: Signer identities aren’t exposed on-chain.
Operationally flexible: You can add/remove signers, change thresholds, or move shares without resetting the wallet.

MPC vs. Multi-Sig: A Detailed Comparison
How Keys Are Secured
- Multisig: Each signer has a full private key. The wallet requires multiple full keys to sign.
- MPC: One private key is split into pieces (shares), and no single piece can sign alone. Signatures are generated through a collaborative computation.
Blockchain Compatibility
- Multisig: Supported only on certain chains and in different ways.
- MPC: Chain-agnostic. Works across any blockchain.
Upgradeability & Flexibility
- Multi-Sig: Modifying signers usually means deploying a new contract (in Ethereum) or setting up a new wallet (in Bitcoin).
- MPC: More dynamic. You can update participants, thresholds, or policies without changing the wallet address or contract.
This matters for growing teams. If your signer setup changes (e.g., someone leaves or joins), updating a multisig wallet is a hassle. MPC is built to evolve with you.
Transparency & Privacy
- Multi-Sig: Signature structure is often visible on-chain. Anyone can see how many parties signed.
- MPC: All signing happens off-chain. This keeps signer identities and rules confidential, which can be important for privacy or security-sensitive operations.
Setup & Infrastructure
- Multisig: Relatively easier to set up, especially with native wallet support.
- MPC: Requires integration with MPC protocols or providers (e.g., Fireblocks, Fystack).
Business Use Cases
- Multisig: Still useful for simple DAO governance, treasury operations, and small teams.
- MPC: Ideal for institutions needing scalability, compliance, flexibility, and operational security.
Multisig vs MPC Wallet: Key Differences
| Criteria | Multisig Wallet | MPC Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Cost (Gas Fees) | Higher. Multisig transactions often require multiple on-chain signatures or smart contract execution, increasing gas costs. | Lower. MPC signing happens off chain, resulting in a single standard transaction on chain. |
| Blockchain Compatibility | Limited. Supported only on blockchains with native multisig or smart contract support. | Chain agnostic. Works across any blockchain that supports standard cryptographic signatures. |
| Security Model | Multiple full private keys are stored independently. Compromise of a key still introduces risk. | No full private key is ever created or stored. Signing is distributed across key shares. |
| Flexibility | Low. Changing signers or thresholds often requires redeploying contracts or creating new wallets. | High. Signers, policies, and thresholds can be updated without changing wallet addresses. |
| Implementation Complexity | Lower initial setup, but complexity increases as governance and transaction volume grow. | Higher initial integration, but significantly simpler to operate at enterprise scale. |
Cost Considerations: MPC Wallet vs Multisig
From a cost perspective, the difference between multisig and MPC wallets is not limited to setup fees or tooling expenses. The real cost emerges over time through operational overhead and organizational friction.
Multisig wallets are often cheaper to deploy initially. They rely on native blockchain features or simple smart contracts. However, as transaction volume grows, multisig introduces hidden costs. These include manual coordination between signers, downtime during signer changes, and the risk of redeploying wallets or contracts when governance structures evolve.
MPC wallets, especially enterprise grade MPC wallet platforms, typically require higher upfront investment. This may include infrastructure, integration, or service fees. In return, they reduce long term operational costs by enabling automation, policy driven approvals, and seamless signer updates without disrupting wallet addresses or workflows.
For teams operating payment systems, treasury automation, or high frequency transaction flows, MPC wallets often deliver a lower total cost of ownership over time.
Which Wallet Model Should You Choose?
The choice between an MPC wallet and a multisig wallet depends less on ideology and more on operational reality.
Choose a multisig wallet if your organization has a small number of signers, operates on a single blockchain, and rarely changes its governance structure. Multisig remains effective for DAOs, static treasuries, and low frequency asset management.
Choose an MPC wallet if your organization manages frequent transactions, operates across multiple blockchains, or requires flexible governance. Enterprises building payment rails, fintech products, or treasury systems benefit from MPC wallets due to their scalability, privacy, and policy driven control.
For teams planning long term growth, MPC wallets are often adopted earlier to avoid costly migrations as complexity increases.
Real-World Examples
Multi-Sig in Action:
- DAOs using Gnosis Safe to manage shared treasuries
- Cold storage custody solutions that require board-level approval for asset movement
MPC in Action:
- Fireblocks securing billions in institutional crypto trades using MPC
- Cobo's custody solutions offering off-chain governance via MPC
- Teams splitting key shares across co-founders or departments to improve resilience and avoid insider risks
FAQ
What is the main difference between MPC and multisig wallets?
Multisig wallets rely on multiple full private keys signing a transaction. MPC wallets split a single private key into shares and generate signatures collaboratively without ever reconstructing the full key.
Do MPC and multisig both remove single points of failure?
Yes, but in different ways. Multisig distributes authority across multiple keys, while MPC removes single key exposure entirely by never creating a complete private key.
Which approach is more flexible for growing teams?
MPC is generally more flexible. It allows teams to change signers, thresholds, and policies without redeploying contracts or changing wallet addresses, which is difficult with multisig setups.
Is multisig still a valid solution today?
Yes. Multisig remains effective for simple governance structures, DAOs, and environments where signer configurations rarely change. Its limitations appear as operational complexity increases.
Why is MPC considered chain agnostic?
MPC operates at the cryptographic signing layer rather than relying on blockchain specific smart contracts. This allows it to work consistently across different chains and networks.
How does MPC improve privacy compared to multisig?
MPC signing happens off chain, so signer identities, approval thresholds, and governance rules are not exposed on the blockchain. Multisig transactions often reveal this information publicly.
Which wallet model is better for enterprise payments and treasury?
MPC is typically better suited for enterprise payments, automated workflows, and high volume transaction systems. Multisig can become operationally rigid in these environments.
Does using MPC mean giving up control to a third party?
Not necessarily. MPC can be deployed as SaaS, self hosted, or hybrid models. Control depends on who holds the key shares and who defines signing policies.
Can teams migrate from multisig to MPC?
Yes, but it requires careful planning. Differences in key structure and signing logic mean migrations should be treated as architectural changes rather than simple wallet upgrades.
When should a team choose MPC over multisig?
Teams should consider MPC when they need cross chain support, frequent signer changes, policy driven approvals, or scalable payment and treasury operations.
Conclusion
MPC and multisig wallets both aim to eliminate single points of failure in crypto key management, but they serve different stages of organizational maturity.
Multisig offers a proven, protocol level approach for simple governance. MPC wallets provide the flexibility, scalability, and operational resilience required by modern enterprises.
Understanding these trade offs allows teams to choose not only what works today, but what will continue to work as their crypto operations scale.
Secure your crypto operations with Fystack
Fystack delivers modern wallet infrastructure for teams and startups - powered by MPC, built for enterprise-grade security and multi-chain flexibility.
No seed phrases. No multisig headaches. Just seamless, policy-driven crypto and stablecoin treasury management. → Sign up at fystack.io to create your first secure MPC wallet.